Half Duplex vs Full Duplex: main differences and operation

In telecommunications we can find multiple terms and characteristics that allow communication to take place normally. In this article we are going to talk about Duplex. More specifically, we are going to see the differences between Half Duplex and Full Duplex. Basically we can say that it allows communications to use simultaneous sending and receiving channels.
What does Duplex mean in communications
First of all we are going to explain what the term Duplex means. It refers, by itself, to the ability to send and receive data. Duplex is often used when talking about conversations over the phone or computer equipment.
This, therefore, is the system that allows two-way communications to be maintained, something that is basic today, as it is able to receive and send messages simultaneously.
However, the ability to be able to transmit in Duplex mode is conditioned by different levels. One of these levels is the physical medium to be able to transmit in both directions, also the transmission system to be able to send and receive at the same time and finally the protocol or communication standard that you use.
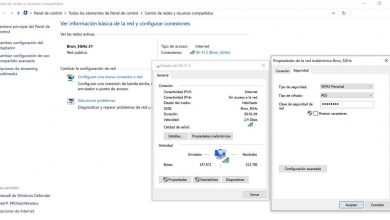
We can find different possibilities. Let’s see how Full Duplex and Half Duplex differ. These are two terms that can appear when configuring a network, especially in systems like Windows, and it is good to know exactly what each one means and which one we could choose to make the most of the available resources.
Differences between Full Duplex and Half Duplex
Full Duplex
On the one hand we can begin to explain what Full Duplex means . This term describes the simultaneous transmission and reception of data through a channel. A device that is Full Duplex is capable of bidirectional network data transmissions at the same time. You are not going to have to wait and verify if it is being broadcast in one direction.
In Full Duplex, as it is translated in Spanish, it has better performance by doubling the use of bandwidth. An example of the use of Full Duplex is on a telephone. Here the communication is simultaneous and bidirectional. It is also present in network switches.
We can take as an example a two-way road. Cars can pass through in both directions. The same happens with communication in Full Duplex. That is why this transmission mode offers better performance. It is what we will find in the fastest connections and devices compatible with them.
Regarding Internet connections, there is a point to take into account and that is that wired connections, those that connect Ethernet cables, are Full Duplex. This thus enables better speeds to be obtained. It basically means that we can send and receive simultaneously, without waiting.

Half Duplex
On the other hand we have the option of Half Duplex. These types of devices can only transmit in one direction at a time. With this mode, data can move in two directions, but not at the same time. Therefore communication is bidirectional, but one at a time. This, as we can imagine, is less optimal than the previous case.
We can say that it offers a lower performance compared to Full Duplex for what we mentioned. An example of how to use it would be a walkie-talkie. They can both talk, but not at the same time. One has to wait for the other to finish. They could not establish communication at the same time, in both directions, as we could achieve with a mobile phone.
Let’s imagine again a highway with two lanes. Vehicles can go one way and another, but not both at the same time. That is to say, the cars going in one direction would have to wait for all those going in the opposite direction to pass and then continue the march. A bottleneck could occur.
These Half Duplex networks will require a mechanism to avoid data collisions. You need to check if there is something transmitting before trying to send something to avoid problems. One device that uses this option is a hub. We see that there is an important difference compared to a network switch. It could not serve us in certain cases in which we are going to require it to be Full Duplex.
The Half Duplex or half duplex mode is the one present in Wi-Fi networks. We already know that wireless networks are increasingly present in our day to day and have improved significantly in recent years, but they continue to have certain problems in terms of stability and do not achieve the same speed as wired networks. They are also required in Internet hubs.
In this case we can find ourselves with the risk of collision. It means that more than one user or one device tries to communicate at the same time but, as we have seen, it is not possible. This can lead to problems, outages, waiting, and certain errors. This forces to implement a system to avoid these collisions and that the communication flows correctly.
Thanks to this system to detect collisions, the devices will detect that there has been a collision and the transmissions will stop for the necessary time and later transmit again. This will allow both devices to broadcast at the same time and generate issues as mentioned. The objective is none other than to avoid those collisions in the transmission. Therefore, in a system that allows to foresee this problem, it will analyze before sending the transmission. In case the channel is free, it will continue; if, on the other hand, it is busy, it will wait until it is free and that way this collision does not occur.
Ultimately we can say that the main difference between Half Duplex and Full Duplex is that communication goes in one direction or both simultaneously. In addition to this key difference, the rest is in the mode of use and in the situations in which we are going to use one or the other option. Some devices, moreover, can only work in one mode or another. That can be decisive in some circumstances.